Genes associated with cell cycle and mitosis are enriched among targets Biology Diagrams Explore the intricate stages of the cell cycle, from growth and DNA replication to chromosome alignment and division, and understand its regulation. In the S phase of the cell cycle, the primary task is the replication of DNA, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an exact copy of the genetic material. This phase is marked by a highly The cell cycle is the process a cell undertakes to replicate all of its genetic material and divide into two identical cells. In this article, we will look at the different stages of this and what happens in each stage. We will also consider the regulation of the cell cycle, and look at some examples of its dysregulation.

The cell cycle is the sequence of events occurring in an ordered fashion which results in cell growth and cell division. G0, G1, S, G2, M. A cell entering the M phase has a 4N concentration of genetic material and ends with two cells, each containing a 2N concentration of DNA. Mitotic cell division occurs via four distinct steps; Proper regulation of these events is crucial for cell cycle timing and preventing uncontrolled cell division, which can lead to cancer. S Phase (DNA Replication) The S phase is dedicated to the accurate replication of the cell's DNA, ensuring that daughter cells inherit a complete set of genetic instructions. The cell cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell that drives it to divide and produce two new daughter cells. Through more than 100 years of efforts by scientists, we now have a much clearer picture of cell cycle progression and its regulation. The typical cell cycle in eukaryotes is composed of the G1, S, G2, and M phases.

An Overview of the Cell Cycle Biology Diagrams
The cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells. It is sometimes referred to as the "cell division cycle" for that reason. When the S phase is completed, the cell will have two complete sets of its genetic material. This is crucial for cell division, as it ensures that both Cell cycle is the name we give the process through which cells replicate and make two new cells. Cell cycle has different stages called G1, S, G2, and M. G1 is the stage where the cell is preparing to divide. To do this, it then moves into the S phase where the cell copies all the DNA. So, S stands for DNA synthesis.
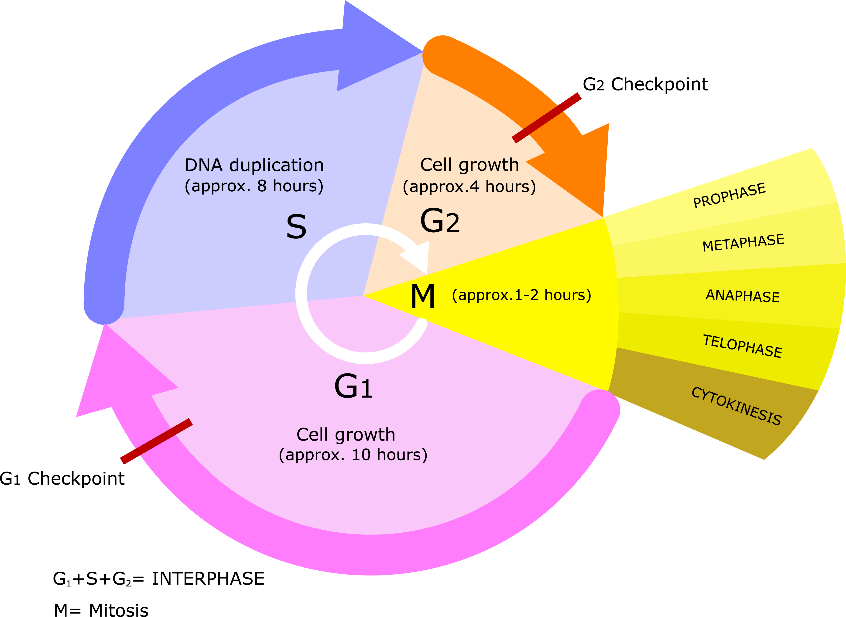
The function of the cell cycle is to prepare the cell for future division. Imagine a cell dividing without growing and reproducing the cellular machinery. Each round of cell division will result in a gradual decrease in the daughter cell, which becomes half in size of the parent cell. The genetic material also reduces in the daughter cell. Figure 2. The cell cycle can be divided into 4 stages: G 1, S, G 2, and M, in order.G 1, S, and G 2 collectively make up interphase of the cell cycle. Cells can also exit the cell cycle into the non-dividing phase of G 0.. Although there is not much change visible under the light microscopy during interphase, in fact the cell performs a carefully orchestrated series of tasks during this time.
