Ecology Williams Biology Diagrams Food-chain length typically is estimated as (1) connectance-based FCL—an average connectance between basal resources and top consumers, (2) functional FCL—by experimental determination of functionally significant effects of a top predator on lower trophic-level biomass patterns, and (3) realized FCL—an average connectance measure weighted

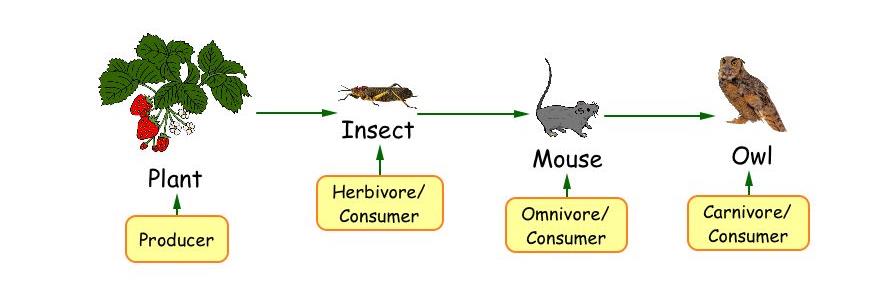
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher-level consumers, and finally decomposers. These levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. There is a single path through a food chain.
.jpg)
Food chain, food web and ecological pyramids Biology Diagrams
Finding an elegant form or process, say the way leaves collect water, carbon, and sunlight to create food, energy, and oxygen, we may simply mimic that form or process. This is called biomimicry, and while its results may sometimes seem largely about aesthetics, they may also lead to practical improvements in sustainability.
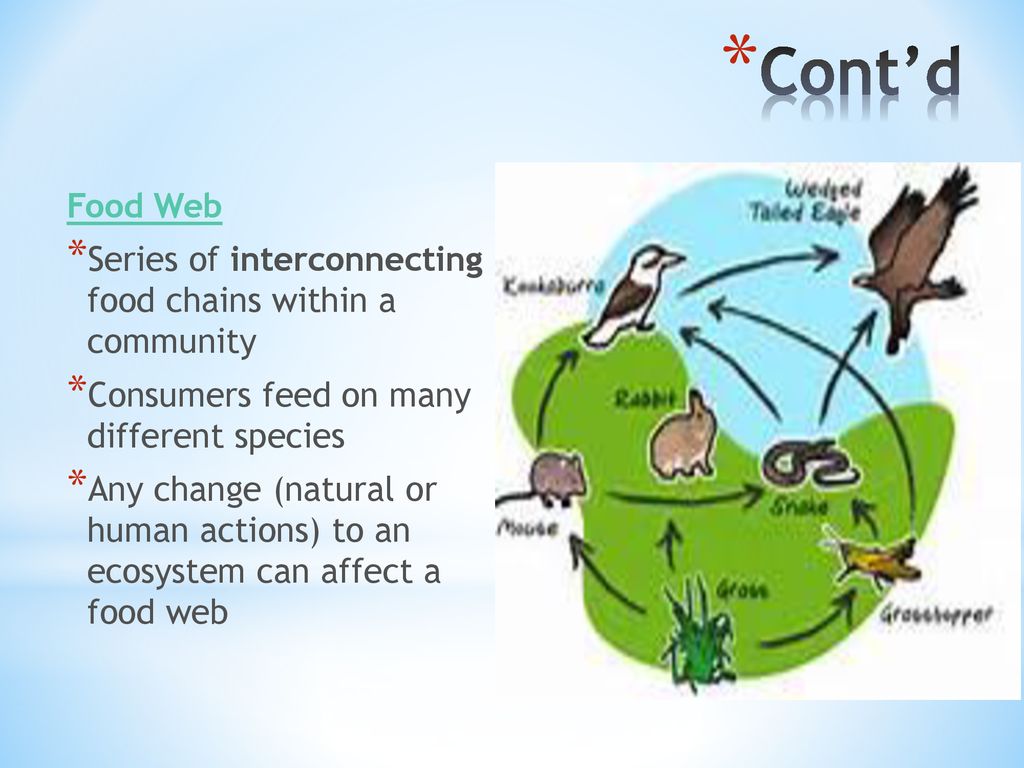
In ecology, a food web describes the feeding connections between organisms in a biotic community. Both energy and nutrients flow through a food web, moving through organisms as they are consumed by an organism above them in the food web. It is rare to find food chains that have more than four or five links because the loss of energy limits 13 Food webs and other networks. A food web is a real or a model of a set of feeding relations among species or functional groups.This chapter has two foci, (i) a very brief introduction to multi-species webs as networks, and (ii) a re-examination of old lessons regarding the effect of food chain length on a web's dynamical properties.
Exploring the Intriguing Similarities Between Food Chains and Food Webs Biology Diagrams
A food chain represents a linear sequence in which energy transfers from one organism to another. Each step in the chain involves a transfer of energy from a source, usually the Sun, through various organisms. Food chains start with primary producers, such as plants, and end with top predators or decomposers, which help recycle nutrients back
